yoooniverse
[kaggle] Learn Tutorial_Pandas (정리)_1 본문
< 3 > Summary Functions and Maps
Pandas provides many simple "summary functions" (not an official name) which restructure the data in some useful way.
Summary functions
1. describe( ) method
type-aware: its output changes based on the data type of the input.
#describe() method: type-aware
#shows an overview of the data
wine_reviews.points.describe() # numerical data
wine_reviews.taster_name.describe() # string datacount 129971.000000 count 103727
mean 88.447138 unique 19
std 3.039730 top Roger Voss
min 80.000000 freq 25514
25% 86.000000 Name: taster_name, dtype: object
50% 88.000000
75% 91.000000
max 100.000000
Name: points, dtype: float642. mean( ), unique( ), value_counts( )
: to get some particular simple summary statistic about a column in DataFrame or Series
- mean( )
- unique( ): to see a list of unique values
- value_counts( ): to see a list of unique values & how often they occur in the dataset
#mean(), unique(), value_counts()
wine_reviews.points.mean() #88.44713820775404
wine_reviews.taster_name.unique() #array(['Kerin O’Keefe', 'Roger Voss', 'Paul Gregutt', ... , 'Christina Pickard'], dtype=object)
wine_reviews.taster_name.value_counts()
'''
Roger Voss 25514
Michael Schachner 15134
Kerin O’Keefe 10776
Virginie Boone 9537
Paul Gregutt 9532
Matt Kettmann 6332
Joe Czerwinski 5147
Sean P. Sullivan 4966
Anna Lee C. Iijima 4415
Jim Gordon 4177
Anne Krebiehl MW 3685
Lauren Buzzeo 1835
Susan Kostrzewa 1085
Mike DeSimone 514
Jeff Jenssen 491
Alexander Peartree 415
Carrie Dykes 139
Fiona Adams 27
Christina Pickard 6
Name: taster_name, dtype: int64
'''Maps
a function that takes one set of values and "maps" them to another set of values.
1. map( )
수학의 합성 함수 개념과 같다
review_points_mean = wine_reviews.points.mean()
wine_reviews.points.map(lambda p: p - review_points_mean)
'''
0 -1.447138
1 -1.447138
2 -1.447138
3 -1.447138
4 -1.447138
...
129966 1.552862
129967 1.552862
129968 1.552862
129969 1.552862
129970 1.552862
Name: points, Length: 129971, dtype: float64
'''
2. apply( )
the equivalent method if we want to transform a whole DataFrame by calling a custom method on each row.
def remean_points(row):
row.points = row.points - review_points_mean
return row
wine_reviews.apply(remean_points, axis='columns')
apply( ) 파라미터 axis='index'
: instead of passing a function to transform each row, we would need to give a function to transform each column.
🚨 map( ) and apply( ) return new, transformed Series and DataFrames, respectively.
🚨 They don't modify the original data they're called on.
+) additional mapping operations
review_points_mean = wine_reviews.points.mean()
wine_reviews.points - review_points_mean
'''
0 -1.447138
1 -1.447138
2 -1.447138
3 -1.447138
4 -1.447138
...
129966 1.552862
129967 1.552862
129968 1.552862
129969 1.552862
129970 1.552862
Name: points, Length: 129971, dtype: float64
'''🐧 Maps allow us to transform data in a DataFrame or Series one value at a time for an entire column.
< 4> Grouping and Sorting
we want to group our data, and then do something specific to the group the data is in.
Grouping
1. groupby( )
reviews.groupby('points').points.count()operation:
- Create a group of reviews which allotted the same point values to the given wines.
- For each of these groups, grab the "points()" column and count how many times it appeared
🔑 value_count() is a shortcut to this operation
🔑 groupby( ) can be used at any summary functions
groupby( ) 응용
- 각 포인트 점수마다 가장 작은 price를 가져옴

reviews.groupby('points').price.min()
# to get the cheapest wine in each point value category
- 와이너리 별 리뷰 순서가 가장 첫번째인 와인의 title 정보를 가져옴
reviews.groupby('winery').apply(lambda df: df.title.iloc[0])
# one way of selecting the name of the first wine reviewed from each winery in the dataset

- groupby에 여러 컬럼 값을 넣어도 가능
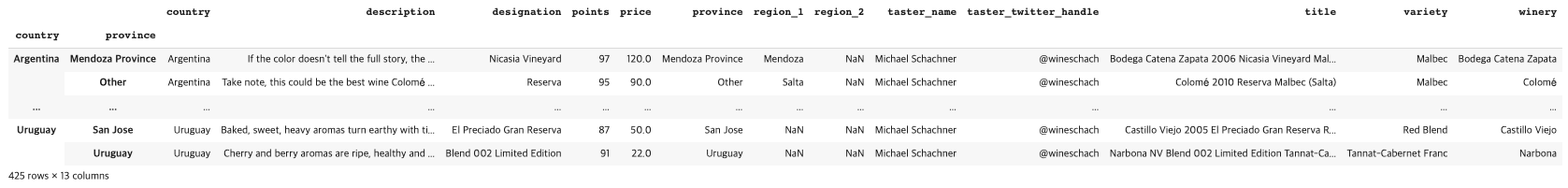
reviews.groupby(['country', 'province']).apply(lambda df: df.loc[df.points.idxmax()]
# picking out the best wine by country and province
(country와 province별 포인트가 가장 높은 와인의 row 정보를 가져옴)
2. agg( )
It lets you run a bunch of different functions on your DataFrame simultaneously
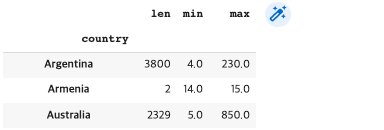
reviews.groupby(['country']).price.agg([len, min, max])
# can generate a simple statistical summary of the dataset나라별 len, min, max 값을 보여준다.(len: 그 나라 와인이 몇 개 인지, min: 그 나라 와인 중 가장 낮은 가격, max: 그 나라 와인 중 가장 높은 가격)
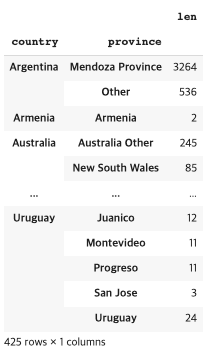
3. multi-indexes
A multi-index differs from a regular index in that it has multiple levels.
require two levels of labels to retrieve a value.
https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/advanced.html
countries_reviewed = reviews.groupby(['country', 'province']).description.agg([len])
countries_reviewed
가장 많이 사용하게 될 멀티-인덱스 메소드 : reset_index( )
countries_reviewed.reset_index()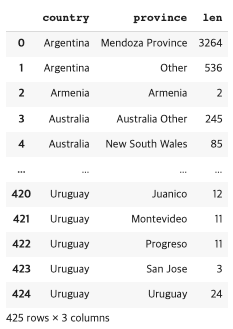
🐧 when outputting the result of a groupby, the order of the rows is dependent on the values in the index, not in the data.
Sorting
1. sort_values()
(1) defaults to an ascending sort, where the lowest values go first
(2) to make descending sort, we use 'ascending = False'
(3) to sort by index, use companion method 'sort_index()
countries_reviewed = countries_reviewed.reset_index()
countries_reviewed.sort_values(by='len')
countries_reviewed.sort_values(by='len', ascending=False)
countries_reviewed.sort_index()
countries_reviewed.sort_values(by=['country', 'len'])
'KAGGLE > Pandas' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [kaggle] Learn Tutorial_Pandas (정리)_0 (1) | 2022.11.11 |
|---|

